(1) Climate-related strategy
The Sompo Group established “SOMPO Climate Action” in FY2021, which include climate change adaptation and mitigation
along with contributing to social transformation as our commitment to implement a comprehensive approach to climate
change risks and opportunities, under which we will promote strategic initiatives throughout the Group.
(1) 1. Climate-related risks and opportunities
In addition to physical risks such as the increased severity and frequency of natural disasters, droughts, and
chronically rising sea levels due to climate change, transition risks may arise as a result of changes in industrial
structures and markets brought about by strengthening of laws and regulations and development of new technologies
for the transition to a carbon-free society that could affect corporate finances and reputations. These risks are
accompanied by an increasing number of climate change lawsuits globally, particularly in the US, that seek to hold
companies legally liable for the impact of climate change resulting from their business activities, investments in
highly carbon-intensive businesses, and improper disclosure. Such lawsuits risk may increase liability insurance
payouts in our P&C insurance business. On the other hand, the growing societal awareness of natural disaster risks
and changes in social structure may bring business opportunities such as the creation of new service demands and
technological innovations.
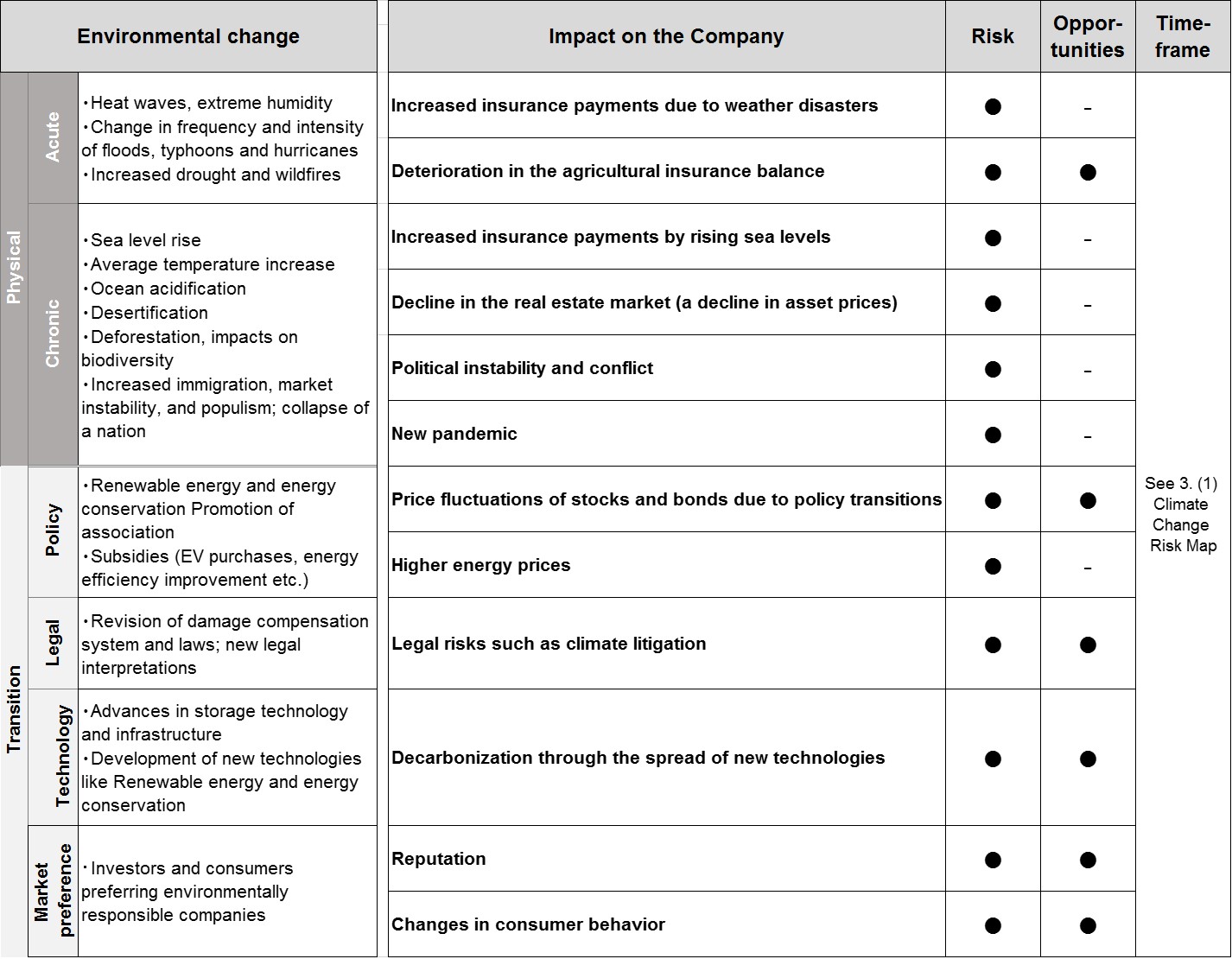
We have identified the risks and opportunities coverage of the entire value chain of
insurance-related business activities (upstream: product/service development, mid-stream: sales/marketing and asset
management, downstream: accident response and payment of claims) that climate change poses to our business based on
the results of studies conducted by external organizations such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
(IPCC) and the Network of Central Banks and Supervisors for Greening the Financial System (NGFS), and we are
assessing, analyzing, and responding to such risks and opportunities on a short- (within 2-3 years), medium- (5-10
years: around 2030), and long-term (10-30 years: around 2050) time horizon. The main environmental changes
associated with physical and transition risks due to climate change, as well as risks and opportunities that are
expected to have a significant impact on the Group, are shown in the table below and are continuously reviewed in
light of changes in the internal and external environment.
(1) 2. Scenario analysiss
A. Physical risks
The Group's P&C insurance business could be financially affected by higher-than-expected insurance payouts due to the
increased severity and frequency of natural disasters, including typhoons, floods, and storm surges. From 2018, we
started working with universities and other research institutions to quantitatively grasp risks based on scientific
findings. Based on large-scale analysis using weather and climate big data, such as the Database for Policy
Decision-making for Future Climate Change (d4PDF)*1, we are working to understand the long-term impacts
of a climate with higher average temperatures with respect to changes in the average trends for storm surges
affected by
typhoons, floods and sea level changes and trends in the occurrence of extreme weather events. We are also analyzing
and evaluating the medium-term impact over the next five to ten years and incorporating this information into our
business strategies.
The Group is a member of the TCFD insurance working group of the United Nations Environment
Programme Finance Initiative (UNEP FI) and estimates the impact related to typhoons using a quantitative
model*2 based on the guidance issued by the working group in January 2021. We will continue our analysis
using the scenario analysis framework being developed by the Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS), which
works on financial regulatory responses to climate change risks.
| Estimate results |
| Frequency of typhoons |
approx. -30% to +30% |
| Amount of damage per typhoon |
approx. +10% to +50% |
We are also analyzing the impact of climate change on natural disasters outside Japan, including US hurricanes and EU
floods, through partnerships with external risk modeling companies and research institutions. We have developed our
own scenarios and are working to apply them to our risk model for natural disasters outside Japan.
*1Database of climate simulations developed by Japan's Ministry
of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology's Program for Risk Information on Climate Change. By using a
number of ensemble simulations, future changes in extreme events such as typhoons and heavy rains can be evaluated
stochastically and with greater accuracy. The results will enable more reliable assessments of the impact on society
of natural catastrophes caused by climate change.
*2Model that captures changes in the frequency and wind speed of
typhoons between now and 2050 based on the RCP8.5 scenario used in the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report (AR5), and
calculates changes in the amount of damage caused.
B. Transition risks
To understand the short-, medium- to long-term impact of the transition to a decarbonized society on our company, we
analyzed the impact on our Group's assets using the Climate Value-at-Risk (CVaR)*3 provided by MSCI for
policy risks
arising from tighter laws and regulations and global economic changes that will affect companies in the transition
to a decarbonized society and technology opportunity arising from climate change mitigation and adaptation
initiatives, based on the NGFS scenarios*4 in the table below.
In addition, since it is important to encourage companies that have not yet made progress in decarbonization efforts
to reduce transition risk, we use the Implied Temperature Rise (ITR)*5 provided by MSCI to quantitatively
analyze whether our portfolio companies have set GHG emission reduction targets consistent with the goal of limiting
global warming to 1.5°C by FY2100.
*3Climate Value-at-Risk (CVaR)
- A method to measure the impact on corporate value associated with climate change-related policy changes and
disasters.
- The future costs and profits arising from climate change-related risks and opportunities are discounted to their
present value, and the impact is calculated as of March 31, 2023, taking into account the market value weighting
of each security in the Group's asset management portfolio.
*4NGFS (Network for Greening the Financial System)
scenarios
Analyzed three climate change scenarios published by the NGFS in November 2023 as Phase 4: Delayed
transition, Net Zero 2050, and NDCs.
| Category |
Scenario |
Summary |
| (1)Disorderly |
Delayed transition |
Assumes annual emissions do not decrease until 2030. Strong policies are needed to
limit warming to below 2°C. Negative emissions are limited. |
| (2)Orderly |
Net Zero 2050 |
Limits global warming to 1.5°C through stringent climate policies and innovation,
reaching global Net Zero CO2 emissions around 2050. Some jurisdictions such as the US, EU, Japan and
etc. reach net zero for all GHGs. |
| (3)Hot House World |
Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) |
Assumes that all policies that countries have committed to are implemented. (It
includes all pledged policies, even if they are not yet implemented, but is insufficient to stop
global warming) |
*5Implied Temperature Rise (ITR)
- One of the forward-looking assessment methods that evaluates the degree of likelihood of 1.5°C and 2°C of global
warming by 2100.
- The contribution to temperature rise is based on the difference between the projected GHG emissions of portfolio
companies (calculated based on current emissions and reduction targets set by the companies) and the carbon
budget, and is calculated as of March 31, 2023, taking into account the market value weight of each stock in the
Group's asset management portfolio.
a. Climate Value-at-Risk (CVaR)
(NGFS scenarios - comparison by asset type)
For all assets, the impact is greatest in the Net Zero 2050
(1.5°C) scenario, which shows that even in an orderly transition, policy risks are significant in order to achieve
the 1.5°C target. In the comparison by asset type, the impact of policy risk and technology opportunity is the
largest for domestic equity, at -37.3% and 7.3% under the Net Zero 2050, respectively. Comparing stocks and bonds,
we see that stocks have a larger impact because bonds never redeem above par value and the impact of policy risk and
opportunity is limited.
<SOMPO Group CVaR analysis of policy risk and technology opportunity by
asset and NGFS scenario>
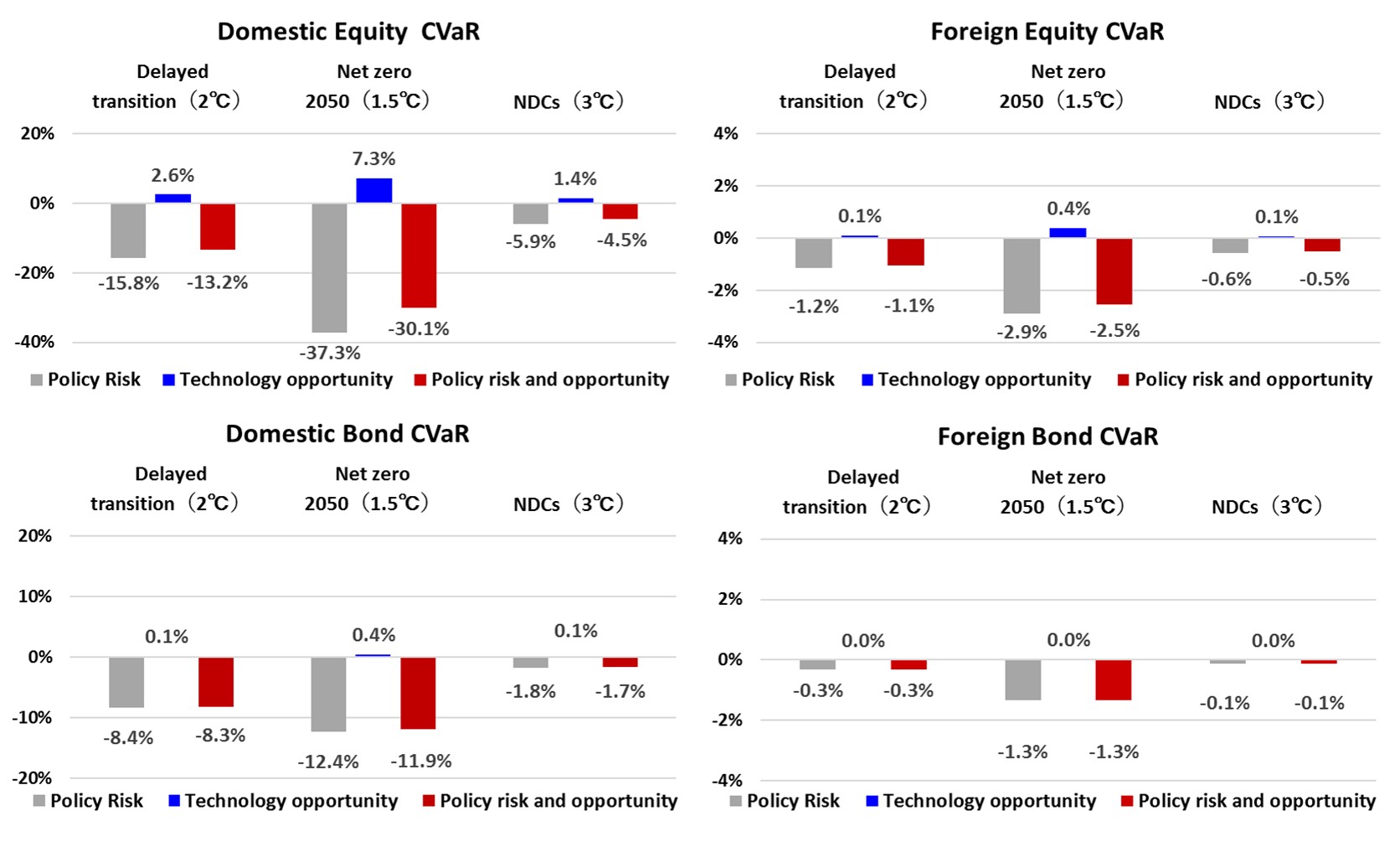
- Policy Risk: Figures calculated for each level of Scope 1, 2, and 3 for the cost required to achieve the
GHG reduction targets.
- Technology opportunity: Figures calculated for the potential business opportunities created by
environment-related technologies owned by companies against the backdrop of the transition to a low-carbon
economy.
(NGFS scenarios - comparison by short-term, medium-term, and long-term time horizon)
Comparing short-term, medium-term, and long-term time horizons, we can see that in our portfolio, the majority of
the current costs will become apparent in the long term (between 2030 and 2050). In particular, the Delayed
transition (2°C) (Disorderly: rapid transition to decarbonization) scenario assumes a rapid policy transition after
2030, so the long-term impact is particularly pronounced. In addition, the policy risk is the highest in the Net
Zero 2050 (1.5°C) scenario at -18.52%, which shows that even in an orderly transition, policy risks are large in the
long term to achieve the 1.5°C target.
<SOMPO Group CVaR analysis results of policy risks and technological
opportunities by time horizon>
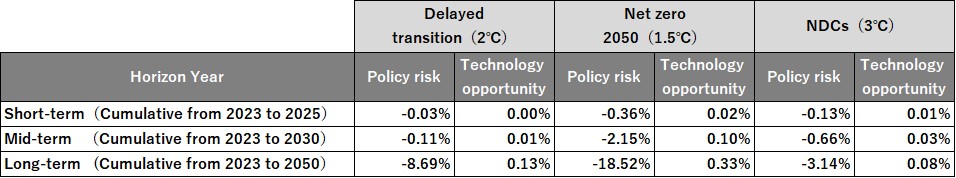
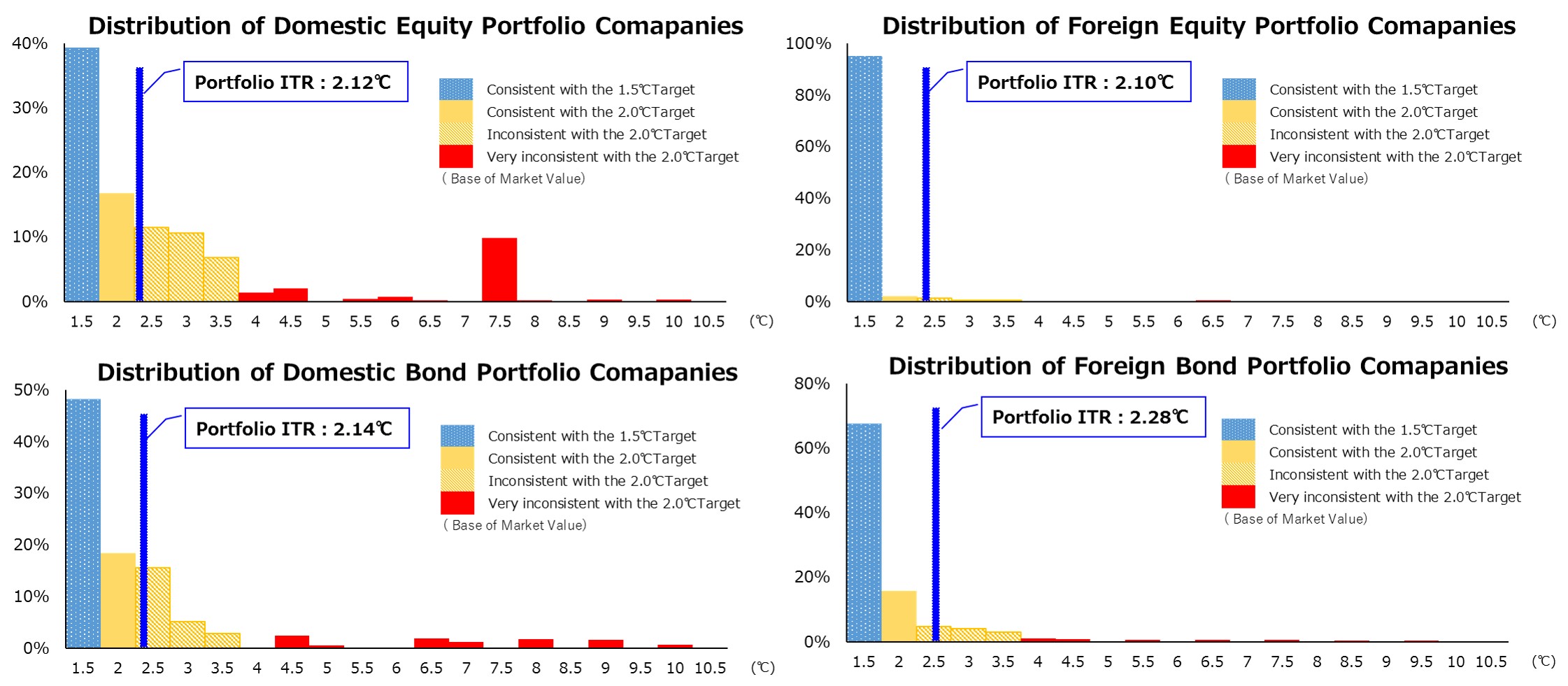
b. Implied Temperature Rise (ITR)
The percentages of companies with ITRs below 2°C are 56% for domestic equity, 97% for foreign equity, 67% for
domestic corporate bond, and 83% for foreign corporate bond portfolios on a market value basis. The percentages of
companies with ITRs below 1.5°C are 39% for domestic equity, 95% for foreign equity, 48% for domestic corporate
bond, and 68% for foreign corporate bond portfolios With the exception of domestic equity, the half of companies
have set GHG emission reduction targets that are consistent with the 1.5°C target set by the Paris Agreement. On the
other hand, for the portfolio as a whole, the ITRs for domestic equity, foreign equity, domestic bond, and foreign
bond are 2.12°C, 2.10°C, 2.14°C, and 2.28°C, respectively, exceeding 1.5°C for all. We will use the results of our
analysis to reduce transition risk by promoting engagement with companies that have high transition risk or have no
GHG emissions targets.
< SOMPO Group ITR analysis by asset >
(Disclaimer)
This report contains information (the “Information”) sourced from MSCI Inc., its affiliates or information
providers (the “MSCI Parties”) and may have been used to calculate scores, ratings or other indicators. The
Information is for internal use only, and may not be reproduced/resold in any form, or used as a basis for or a
component of any financial instruments or products or indices. The MSCI Parties do not warrant or guarantee the
originality, accuracy and/or completeness of any data or Information herein and expressly disclaim all express
or implied warranties, including of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. None of the MSCI
Parties shall have any liability for any errors or omissions in connection with any data or Information herein,
or any liability for any direct, indirect, special, punitive, consequential or any other damages (including lost
profits) even if notified of the possibility of such damages.
(1) 3.Resilience improvement initiatives
A. Responding to risks
<Physical Risk>
Our P&C insurance and reinsurance contracts are primarily short-term contracts, and by
reviewing our insurance underwriting conditions and reinsurance policies in light of the increasingly severe trends
in meteorological disasters, we can reduce the risk of insurance payments exceeding our expectations. We also aim to
ensure resilience against physical risks through a multifaceted approach that includes global geographic
diversification, quantification based on short- and medium-term climate forecasts, and identification and evaluation
of significant risks through long-term scenario analysis.
<Transition Risk>
As for our own GHG emissions, we have set a target of a 60% reduction (compared to
2017)* in Scope 1, 2, and 3 (excluding insurance underwriting, investments and loans) by 2030 and a net
zero emissions by 2050.
To achieve this goal, we have set a target of “70% introduction of renewable energy by 2030,” in addition to energy
conservation efforts such as the use of LEDs for electricity, which accounts for a particularly large portion of GHG
emissions. We are working on the roadmap to achieve this goal, including switching to renewable energy sources for
power generation in our buildings.
- Science-based targets consistent with the Paris Agreement's 1.5℃ target (a reduction of at least 4.2% each year)
As for the GHG emissions of our investees, we are promoting a switch from high GHG emitting sectors to low GHG
emitting sectors at the time of maturity redemption of bonds, and engagement with the top 20 high GHG emitting
companies among our equity holdings.
B. Responding to opportunities
In addition to developing and providing climate risk consulting services and working to improve natural disaster
resilience through insurance products and services, the Sompo Group is developing and providing insurance products
and services that contribute to carbon neutrality by promoting renewable energy and collaborating with business
partners.
We have set a "Transition Insurance Target" for insurance products that contributes to decarbonization in both
domestic and overseas market. In addition, we calculated GHG emissions associated to insurance underwriting
(Insurance-Associated Emissions) using data from companies that disclose GHG emissions (Scope 1, 2) by utilizing a
method for measuring GHG emissions in the commercial insurance sector developed by Partnership for Carbon Accounting
Financials(PCAF) in November 2022.
In accordance with the principles of the Japanese Stewardship Code, Sompo Japan conducts an ESG survey ("Survey on
ESG/Sustainability Initiatives") every year to confirm the policies and status of the companies in which it holds
shares regarding the enhancement of their corporate value and sustainable growth. In fiscal 2023, the survey was
sent to 1,446 companies in which it holds shares, and 318 companies responded. The survey is used to understand the
needs of each company and create opportunities for collaboration,
supporting sustainability efforts, including decarbonization.
Various organizations and groups around the world are actively discussing the formulation of regulations and guidance
to realize a net zero society. By proactively participating in and leading these rule-making efforts, the Group will
not only contribute to societal transformation but also seek to create and expand business opportunities for the
Group, such as attracting partners by accumulating knowledge and enhancing our reputation through these efforts.